KYC Compliance: Understand the Why, What, and How
KYC is an acronym for Know Your Customer. As more and more business is being transacted in the cyber world we have seen a rise in the spate of frauds and money laundering activities to fund nefarious acts. There was a growing need to keep a check on these. Reserve Bank of India, in a bid to curtail these came out with KYC guidelines for banks in the year 2002 and in the year 2004 made it mandatory for all banks to become KYC compliant by the end of the year 2005.
The objective of KYC is for the Banks to understand the customers better not just in terms of their whereabouts and identity but also knowing their transactional behaviors.
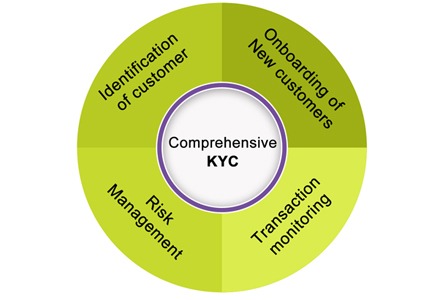
There are roughly four key areas around which the KYC forms need to be built.
- Customer Acceptance Policy
- Customer Identification Procedures
- Monitoring of Transactions and
- Risk management
KYC is a legal and binding activity and one that can be revised time and again depending on the customer profile.
The Procedure:
The process of KYC requires identifying the customer’s address and verifying their identity using reliable documents to gain this information. While opening different accounts the concerned Banks or organizations collect all the relevant documents pertaining to the customer to ensure that the compliance to KYC guidelines issued by the RBI are met.
This is not a comprehensive list and there may be other instances when the financial institutions seek information for KYC compliance from both the new and existing customers.
What Is KYC in the Banking Sector?
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a mandatory process for banks to verify customers’ identities. It helps prevent fraud, money laundering, and financial crimes by confirming that individuals and businesses using banking services are legitimate.
Moreover, banks are legally required to comply with KYC guidelines to:
- Verify customer identities before opening accounts.
- Detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Monitor transactions to identify suspicious patterns.
- Meet KYC compliance regulations set by financial authorities.
Situations That Require KYC
Know Your Customer (KYC) is mandatory in several banking and financial scenarios to verify identities, prevent fraud, and comply with regulatory requirements. Here are key situations where KYC verification is required:
Opening a Bank Account
Whether it’s a savings, current, or business account, banks require KYC documents such as ID proof, address proof, and financial details before activating an account. Without a completed KYC process, account access may be restricted.
Applying for a Loan or Credit Card
Banks verify identity, income, and creditworthiness using KYC information before approving loans or credit cards. Additional due diligence is conducted for high-risk borrowers to assess potential financial risks.
Large Transactions and High-Value Investments
To prevent money laundering, KYC compliance is required for transactions above a certain threshold. Investors in mutual funds, stocks, or insurance policies must verify KYC before investing, ensuring transparency and regulatory adherence.
Updating Personal or Financial Information
Address, income, or legal status changes require an updated KYC account to maintain compliance. Banks may ask for re-verification if KYC documents are outdated, ensuring records are accurate and up to date.
International Money Transfers
Banks and financial institutions verify sender and receiver details as part of KYC guidelines for cross-border transactions. High-value remittances often require enhanced due diligence to prevent fraud and illegal fund transfers.
Cryptocurrency and Digital Wallets
Many cryptocurrency exchanges and digital payment platforms require KYC compliance to verify users and prevent illegal transactions. Users must submit KYC documents before making deposits or withdrawals to ensure secure and legitimate transactions.
Business and Corporate Accounts
When opening corporate accounts, companies must provide business registration details, tax records, and authorised signatory KYC information. Compliance checks are stricter for businesses operating in high-risk sectors to prevent financial fraud.
Insurance and Investment Policies
Insurance companies require Know Your Customer (KYC) verification before issuing policies to verify the legitimacy of policyholders. Investors in mutual funds, bonds, or alternative assets mustalso meet KYCr requirements before making transactions to comply with financial regulations.
KYC – What do banks require from individuals?
For being KYC compliant for individual accounts, Banks require the following information and documents corroborating the same:
1. Legal name and any changes in the name made thereof
2. Correct and full permanent address
The prospective or existing customers must present the original documents for verification and submit a copy to the bank for record-keeping. These may include:
Identity Proof (any one of the following documents)
- Passport
- PAN Card
- Voter’s Identity Card
- Driving license
- Ration Card
Address Proof (any one of the following)
- Utility bill (electricity, telephone, waterworks)
- Bank Account statement (received by mail/courier) along with signature verification by the Bank or a cheque drawn on the account
- Ration Card
- Letter from Employer on the Company Letterhead (subject to satisfaction of the bank)
KYC – What do banks require from companies / organizations?
The Documents Required for KYC may vary for Accounts of Companies, Firms, Trusts, Partnerships, etc. Account holders may be requested to furnish their latest color Photographs along with duly filled and signed KYC forms. The banks may also call for periodic updates when they deem fit.
In our busy schedules, KYC compliance has been simplified through the e-KYC process, which means filling out the necessary forms using the e-KYC Service providers who take the burden of keeping a tab on the customers and ensuring verifications. Identification procedures are kept up-to-date and in conformance with the guidelines laid out. They help update, change and maintain the KYC details for you so that the business never suffers. In case of any delays and non-conformance, the bank has the right to consider closing the account or terminating the banking relationship after issuing due notice to the customer.
How ProcessVenue’s Solutions Can Help in Your Growth
Managing KYC compliance can be complex, but it’s essential for fraud prevention, regulatory adherence, and secure customer onboarding. ProcessVenue simplifies this process with efficient, automated solutions that help you stay compliant while focusing on business growth.
Here’s how ProcessVenue supports your KYC compliance:
- Automated KYC Verification: ProcessVenue streamlines customer verification with automated identity checks, reducing manual work and speeding up approvals. This helps you onboard customers quickly while meeting compliance standards.
- Secure Document Management: Protecting sensitive data is critical. ProcessVenue offers encrypted storage and easy retrieval of KYC documents, minimising security risks and unauthorised access.
- Regulatory Compliance Support: KYC regulations change frequently, and non-compliance can lead to penalties. ProcessVenue tracks evolving requirements and ensures your processes align with the latest legal standards.
- Fraud Prevention & Risk Management: Advanced fraud detection tools help identify suspicious activities early, protecting your business from identity theft and financial fraud.
- Seamless Integration: ProcessVenue’s solutions work with your existing systems, ensuring a smooth transition without disrupting operations.
FAQs
What are the 5 stages of KYC?
The Know Your Customer (KYC) process typically involves:
- Customer Identification: Collecting KYC documents such as ID proof, address proof, and financial details.
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): Verifying KYC information to assess risks.
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): Conducting deeper checks for high-risk customers.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Tracking transactions for suspicious activities as part of KYC and compliance efforts.
- Periodic Updates: Regularly updating KYC account details to meet KYC compliance requirements.
What are the 4 pillars of KYC?
The KYC guidelines for financial institutions are based on these four pillars:
- Customer Acceptance Policy (CAP): Defines the criteria for onboarding customers.
- Customer Identification Procedures (CIP): Outlines the KYC verification process.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Ensures that customer transactions comply with KYC compliance norms.
- Risk Management: Helps banks mitigate financial crimes by enforcing strict Know Your Customer requirements.
What are the 3 components of KYC?
The three main components of KYC are:
- Identity Verification – Collecting and verifying customer identity through KYC documents such as passports or driver’s licenses.
- Risk Assessment – Evaluating customer profiles to determine the risk level per KYC compliance requirements.
- Monitoring & Reporting – Tracking account activity to detect suspicious behaviour and meet Know Your Customer requirements for banks.
How do I check my KYC compliance?
You can check your KYC compliance status by:
- Log into your bank KYC portal to verify your KYC information is current.
- Review your KYC account to ensure all required KYC documents are submitted.
- Check with your bank or KYC services provider for any missing updates in your KYC process.
What is the rule 2090?
Rule 2090, also known as the Know Your Customer (KYC) Rule, is a regulation by FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority). It requires financial institutions to verify a customer’s identity and financial profile before opening an account, ensuring that the KYC process aligns with KYC and compliance standards.
Why is KYC so important?
KYC compliance is essential for:
- Preventing fraud: Verifies identities to reduce financial crime.
- Ensuring regulatory compliance: Meets Know Your Customer requirements for banks and financial institutions.
- Reducing risk: Helps assess and mitigate financial and reputational risks.
- Improving security: Ensures only legitimate customers can access banking and financial services.